Running on LUMI
To run interactive jobs on LUMI the srun command can be used. First we allocate resources for the job:
salloc -n 1 -c 1 -t 00:15:00 --job-name=<job_name> --account=project_<id> --partition q_industryThen we run our script
srun python qiskit_flip.pyThe command takes a number of arguments
--account: Unix group string which can be found in your MyCSC project.-t: Sets a limit on total run time of job allocation. Upper bound is 15 minutes.-c: Requests that n CPUs be allocated per process.-n: Number of tasks to run in parallel. If greater than 1, a job may be assigned to multiple nodes.--partition: The partition to run on. Should beq_industry.
Note, that the srun command is blocking, which means that you’ll have to wait until your program terminates before srun returns and you can enter your next command. Alternatively you can also load a shell on the compute node to provide more flexibility. This can be done with the following command:
srun --account=project_<id> -t 0:15:00 -c 1 -n 1 --partition q_industry --pty bashThis command loads a bash shell on the compute node with access to the quantum computers. After getting the shell, you may need to load your modules again.
!!! note
The LUMI Web-interface is now available at [www.lumi.csc.fi](https://www.lumi.csc.fi). You can run jupyter-notebooks through this web interface. [See the section below for further details](#web-interface).To run longer experiments, it is advisable to use sbatch which executes batch jobs on LUMI.
#!/bin/bash
#SBATCH --job-name=quantum-job # Job name
#SBATCH --account=project_<id> # Project for billing
#SBATCH --partition=q_industry # Partition (queue) name
#SBATCH --ntasks=1 # One task (process)
#SBATCH --cpus-per-task=1 # Number of cores (threads)
#SBATCH --time=00:15:00 # Run time (hh:mm:ss)
module use /appl/local/quantum/modulefiles
# uncomment correct line:
# module load helmi_qiskit
# or
# module load helmi_cirq
python your_python_script.pyJob queues
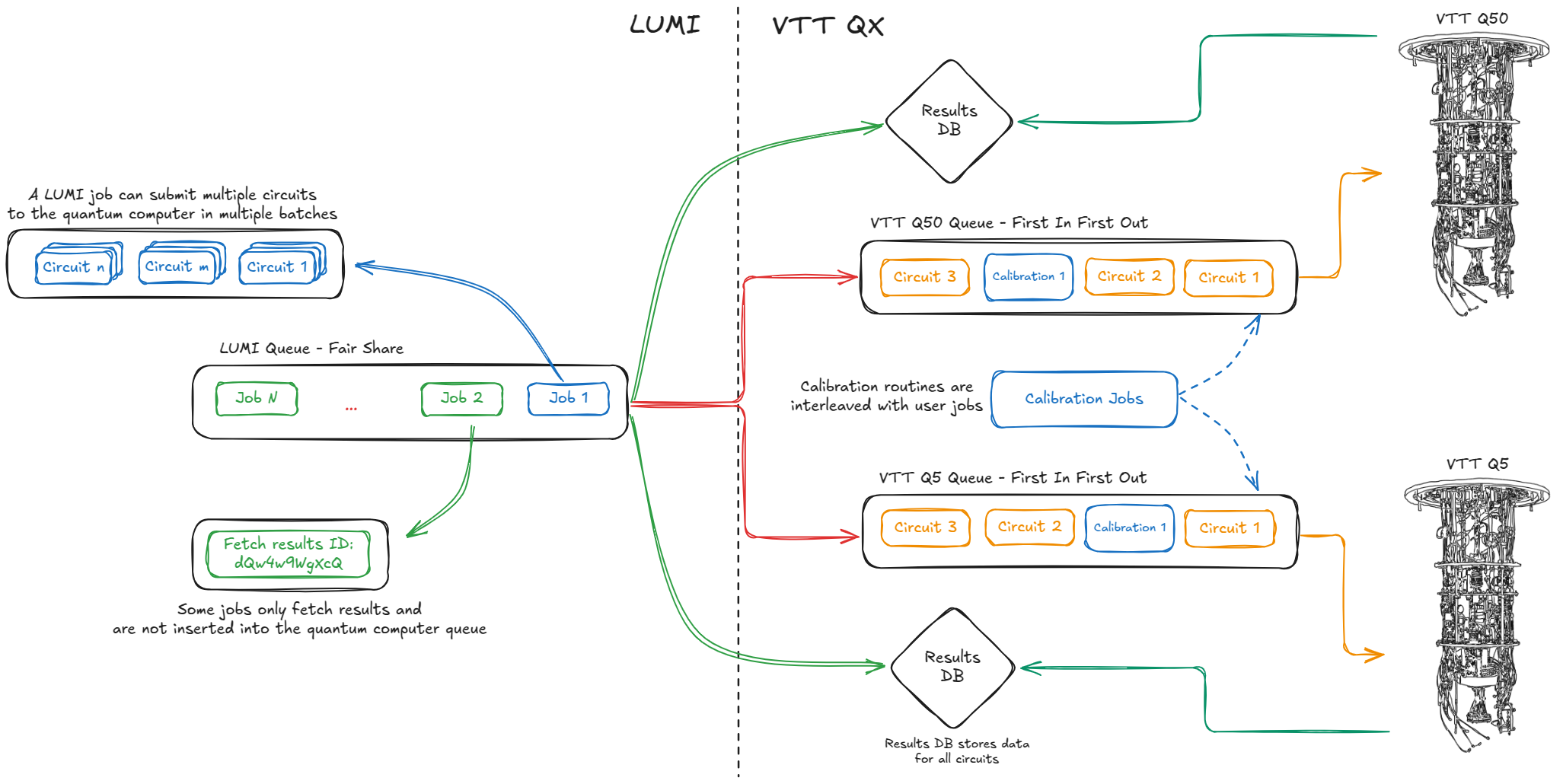
Running on the quantum computers through LUMI involves using two queues. The first one is the SLURM queue on LUMI. Users interact with SLURM using the srun or sbatch commands for job submission and can fetch details about the queue state using squeue -p <partition>. The state of the partition can be viewed with sinfo -p <partition>.
Jobs on LUMI have the following limitations
- Maximum duration for any job is 15 minutes
- Maximum of 32 cores
After your job is accepted by LUMI, it will be allocated to a node within the q_industry partition. At present, the nid002153 node is available for use, which is equipped with 128 CPU cores and 256 GiB of memory.
For additional information:
- To check the `q_industry` partition's current limits and the list of nodes, use `sinfo -s q_industry`.
- To obtain information about the node `nid002153`, use `scontrol show node "nid002153"`.The second queue is the Quantum Computers’s internal job queue. It consists of a simple first-in-first-out (FIFO) queue. Each job from LUMI that executes a quantum circuit on the QC will be inserted into this queue. It’s important to note that operations that retrieve data, such as shot results or calibration data, do not enter this queue. Furthermore, periodic calibration jobs, submitted from VTT’s side, are interleaved with regular user jobs in the respective queues. (see Calibration) as depicted in the picture below.
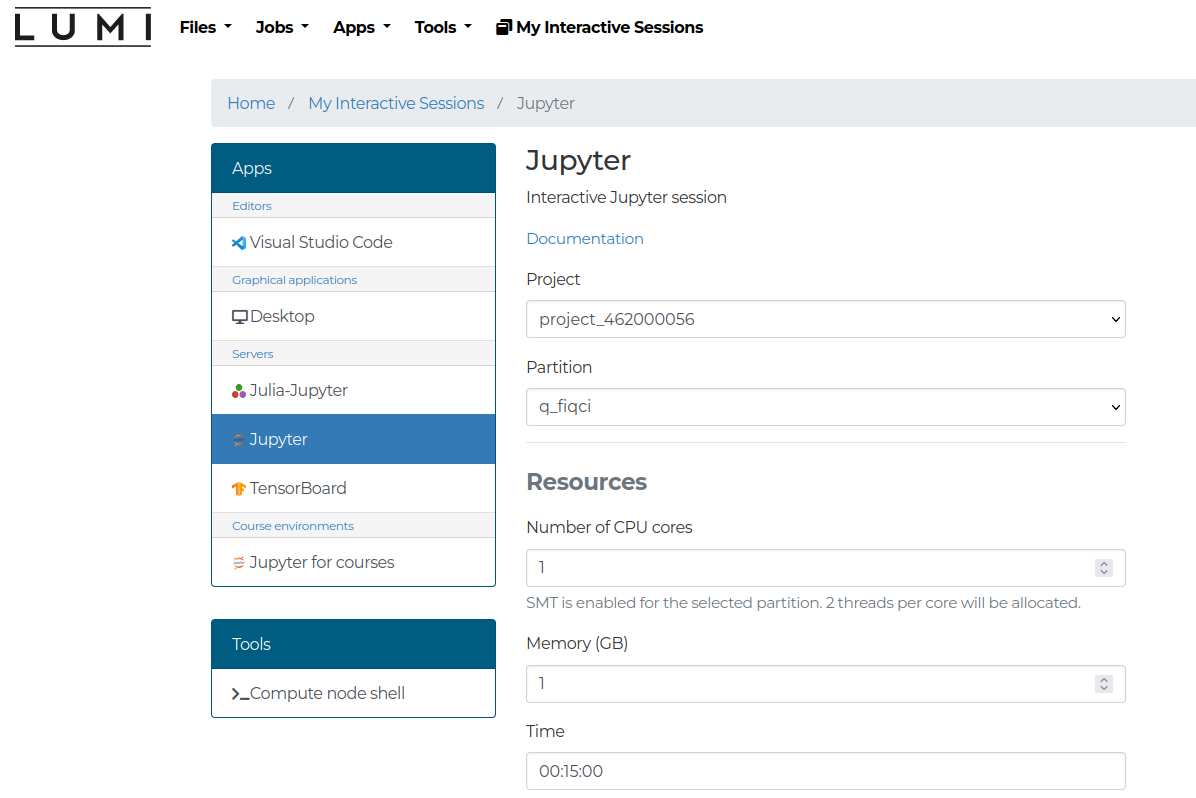
Web-interface
The LUMI Web interface allows users to run on both quantum computers through their browser and use Jupyter notebooks for execution. Here is a brief guide, specifically for Q5, however further details can be found here.
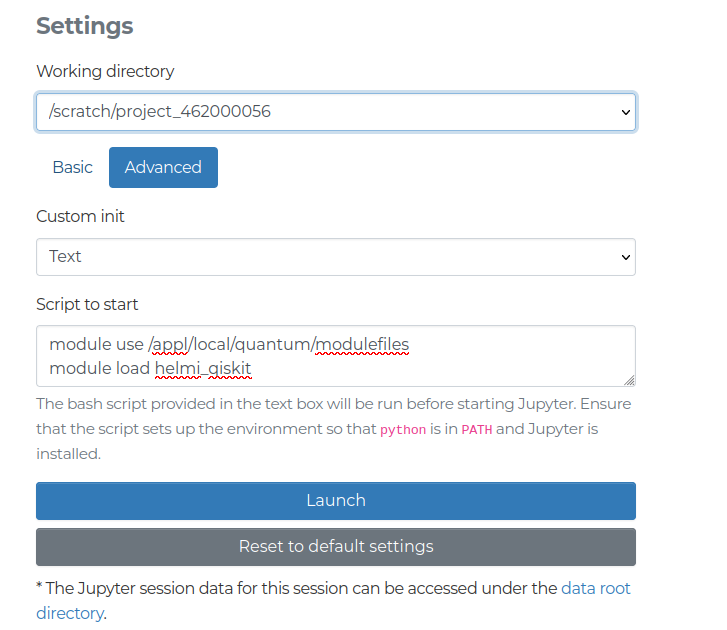
Once you have logged in select the Jupyter option. The session should be configured by selecting your project and the partition. The partitions should be q_fiqci and q_industry for use with QX. The resource limitations are described here. For use with the quantum computers some custom advanced settings should be configured.
module use /appl/local/quantum/modulefiles
module load helmi_qiskitThis pictures below demonstrate the process.